图论 c++
Step1:Basic Theoretical Knowledge
有向图
无向图
连通图
完全图
连通分量
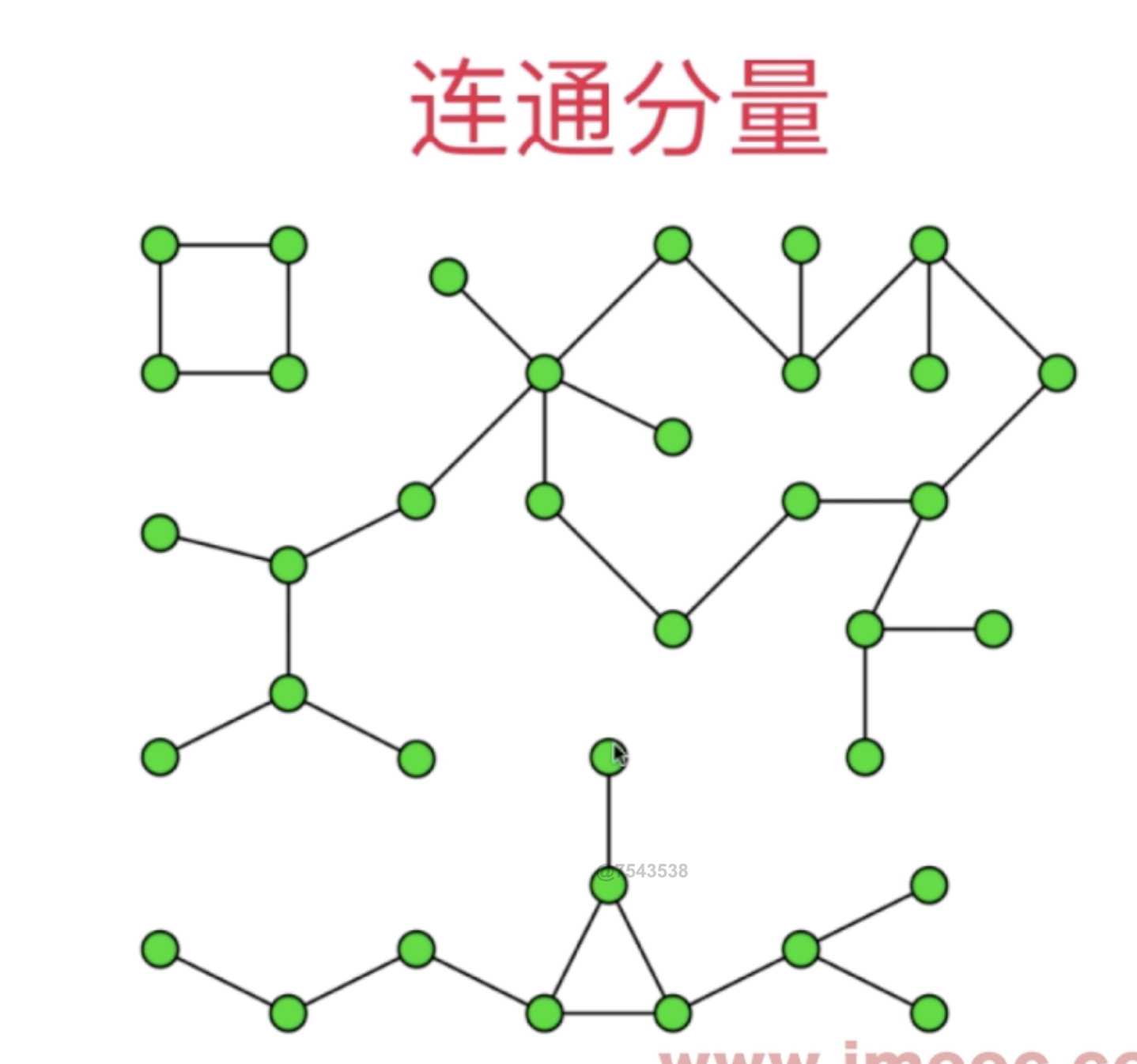
Step2:Demos Of Practice
C++ 稀疏图(临接表实现)
1 | // |
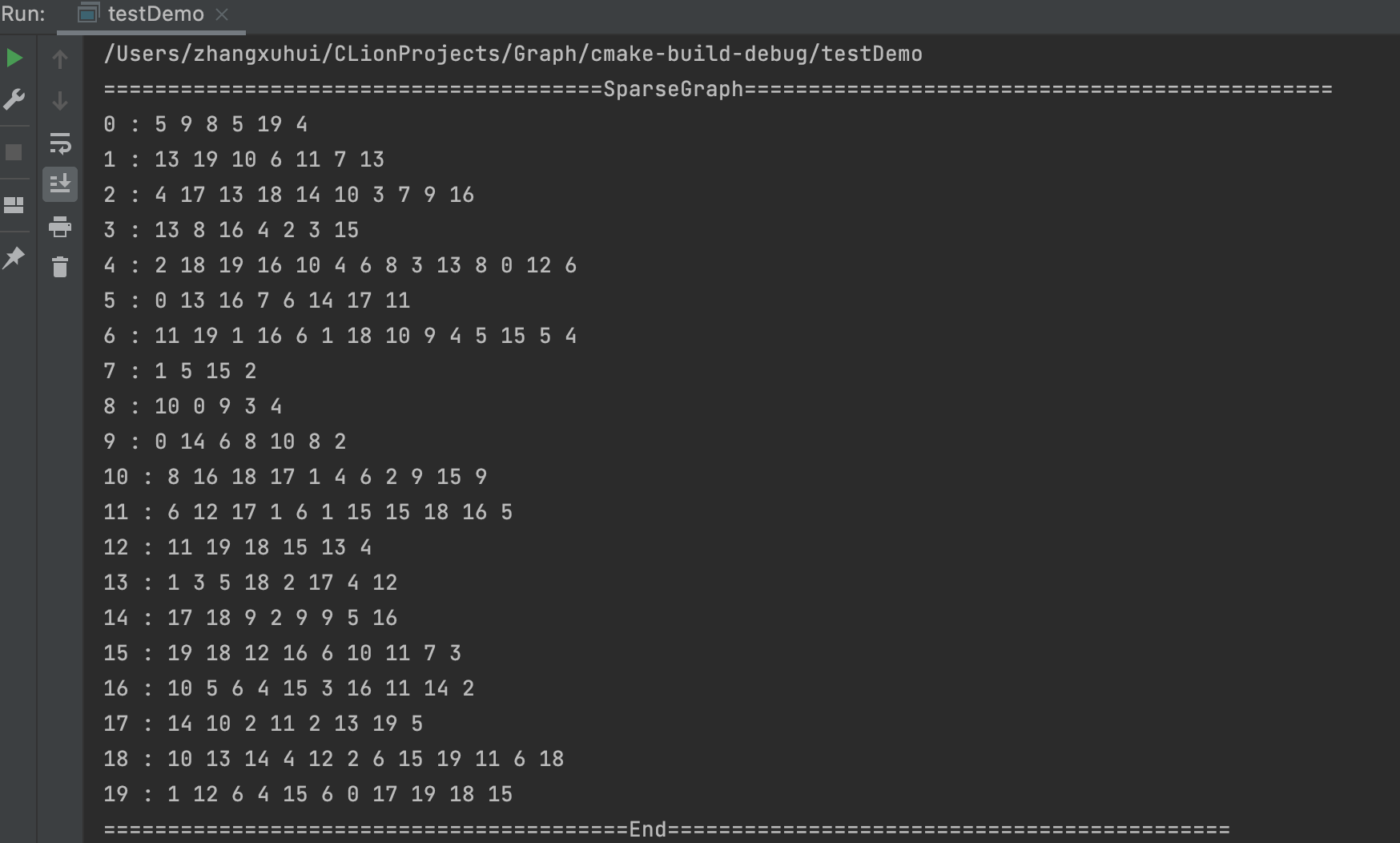
测试稀疏图
1 |
|
结果
C++ 稠密图(邻接矩阵实现)
1 | // |
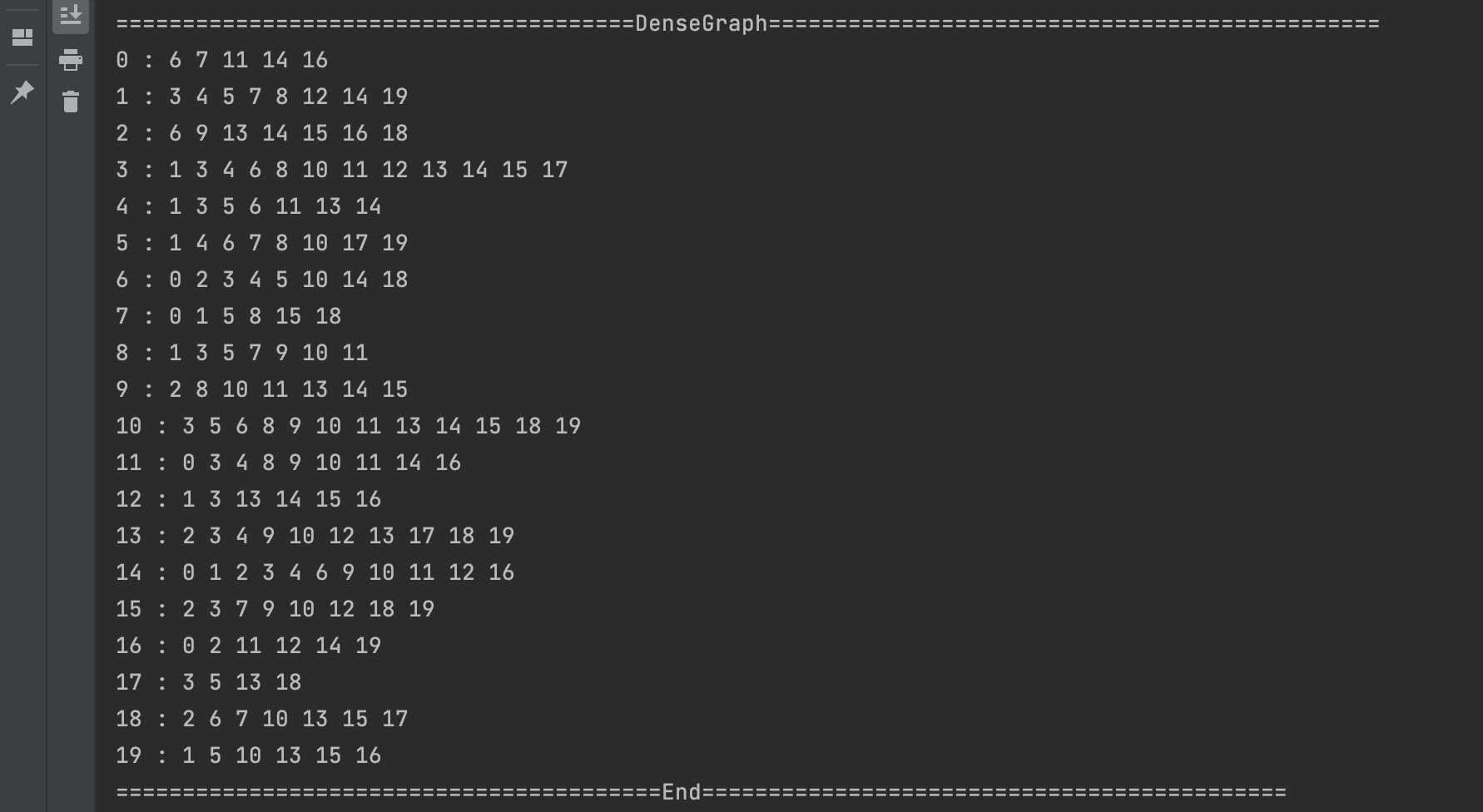
测试稠密图
1 |
|
结果
统一读取数据的头文件 ReadGraph.h
1 | // |
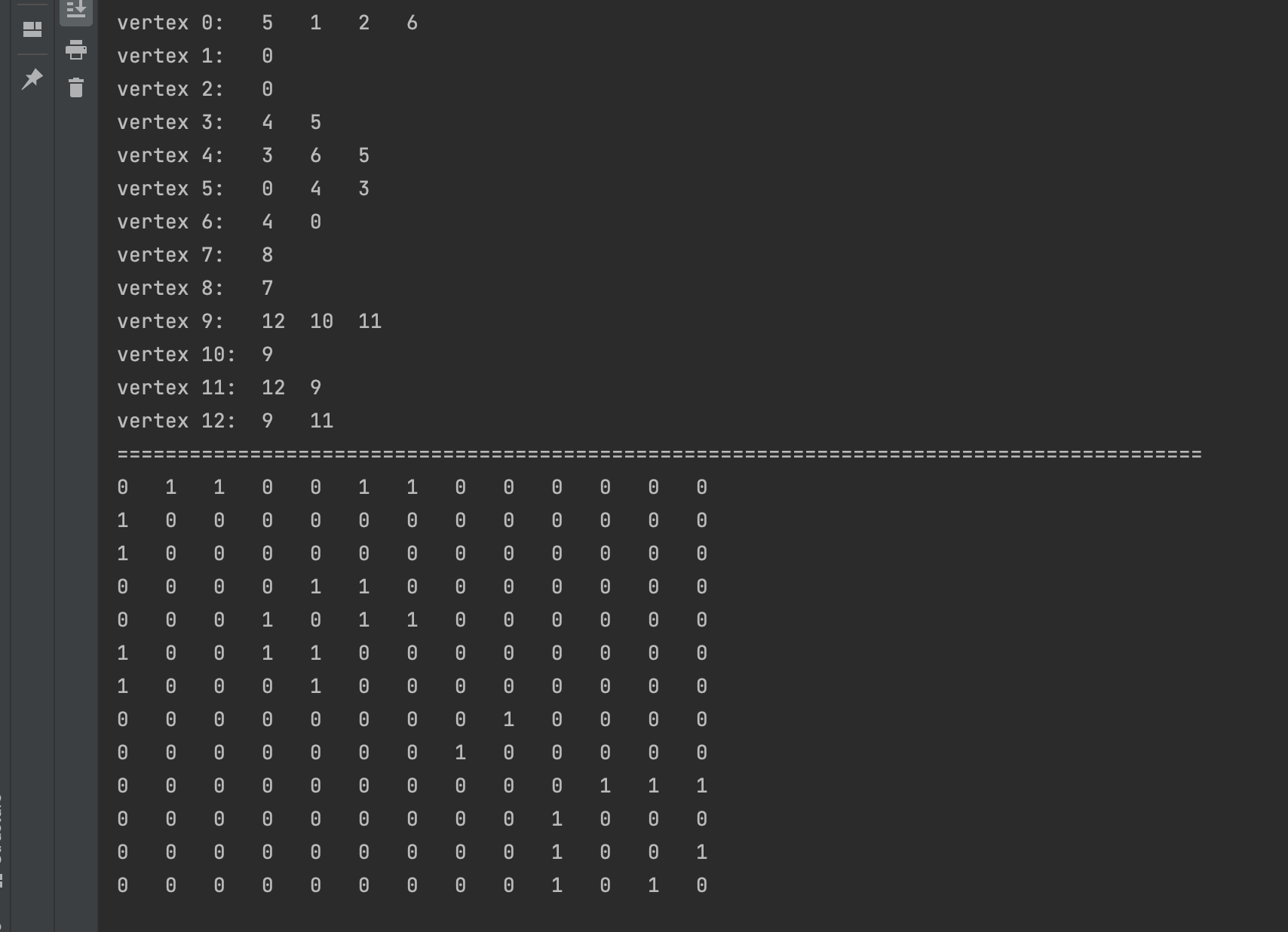
测试读取文件 testG1.txt
testG1.txt
1 | 13 13 |
Main.cpp
1 |
|
结果
Step3: Flexible Use
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 到处皆诗境,随时有物华!
评论




